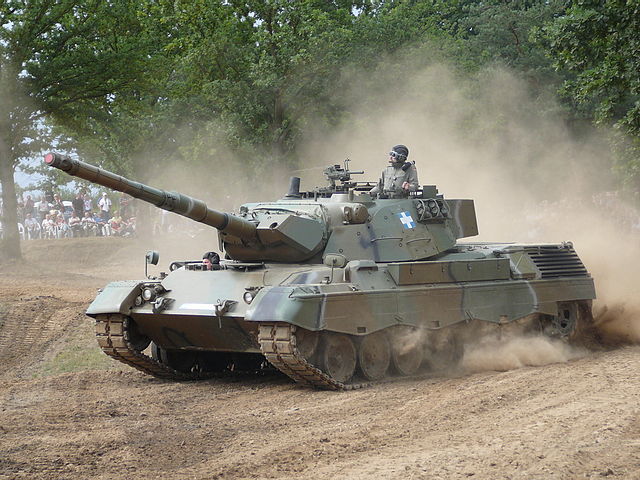
Leopard 1 main battle tank
Leopard 1 is the main battle tank designed by West Germany and France and later joined by Italy. Development started in November 1956 when the operational requirement for a new battle tank was formulated by West Germany, Federal German Armed Forces known as Bundeswehr.
In June 1957 Germany and France signed a co operation agreement to develop a common tank, designated ‘Standard-Panzer’. In September 1958 Italy joined the development program. This partnership was ended and the final design was ordered by the Bundeswehr. Full-scale production started in 1965. In total, 6,485 Leopard tanks have been built, of which 4,744 were battle tanks and 1,741 were utility and anti-aircraft variants. This number does not include 80 prototypes and pre-series vehicles. The building of the first prototype ‘Porschetyp 773’, had already started in September 1960 in anticipation of the official order from the West German Armed forces.
In August 1963 comparative trials were started and lasted for three months between the German and French designed prototypes at Mailly de Camp, Bourges, and Satory in France, and continued in Meppen, Germany. The trials demonstrated that the German tank had the edge over the French AMX-30.
Funding problems prevented the French from purchasing any new tanks before 1965. Change in defense policy and later leaving NATO by France in 1966 ended Franco-German efforts to produce a common or ‘Standard’ – Main battle tank and both countries went on to pursue their own tank development programs. The first AMX-30s were delivered to the French Army in the autumn of 1966. Italy decided to go with the American tank M60A1. On 1 October 1963, the ‘Standard’ tank was officially named “Leopard” later re-designated “Leopard 1” to differentiate it from the “Leopard 2”. On 22 August 1963, West Germany ordered 1,500 Leopards.
The Leopard quickly became a standard of European forces, and eventually served as the main battle tank in over a dozen countries worldwide.
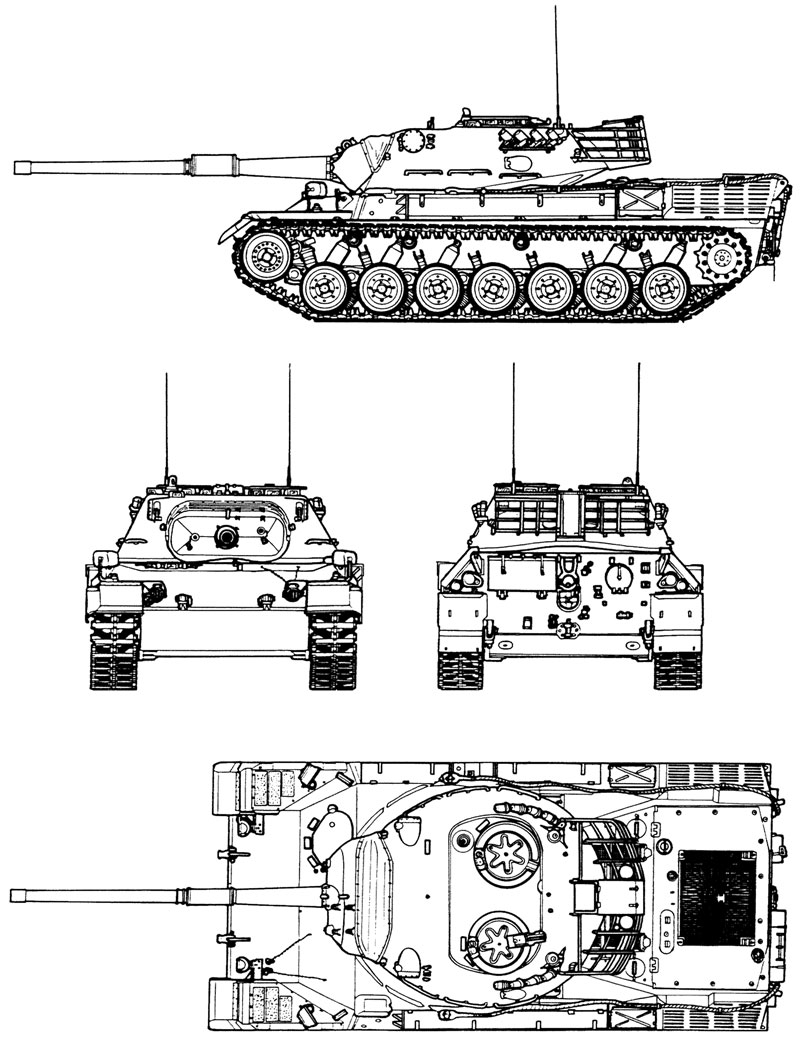
Leopard 1 tank Specifications
Designer: Porsche
Designed: 1956–1961
Produced: 1965–1984
Mass: 42.2 tonnes (increased on later models from original 40.0 tonnes)
Length: 9.54/8.29 m (gun forward/rearward)
Width: 3.37 m
Height: 2.39/2.70 m (turret roof/absolute)
Crew: 4 (commander, driver, gunner, radio operator/loader)
Armour: Steel. 10–70 mm RHAe
Main armament: 1 × 105 mm Royal Ordnance L7A3 L/52 rifled gun (13 rounds in turret 42 rounds in the hull)
Secondary armament:
2 × 7.62 mm MG 3 or FN MAG (co-axial and commander’s hatch) (5500 rounds)
Engine: MTU MB 838 CaM 500, 10-cylinder, 37.4 litres, multi-fuel engine
830 PS (819 hp, 610 kW) at 2,200 RPM
Power/weight: 19.6 PS (14.5 kW) /tonne
Suspension: Torsion-bar
Operational range: 600 km (on-road), 450 km (cross-country)
Maximum speed: 65 km/h

The Leopard 1 has an all-welded hull. The running gear consists of seven wheels per side. The driver’s position is situated to the right front of the hull. Protection is provided by a lift-and-swing type hatch. For driving under armored cover, the driver has three vision periscopes available. The Leopard 1 has IR-sight for night operations. The cast turret is mounted in the center of the hull and is manned by the commander and the gunner with the loader on the left.
An MG 3 is mounted for air defense, in beginning 7.62 mm MG 1 is used. This gun is operated by the loader, who has two observation periscopes available when under armor. A total of 60 rounds are carried for the 105 mm L7A3 rifled gun. Various types of British, American, and German ammunition can be fired, including APDS, HEAT, HESH/HEP as well as smoke, canister, and target illumination rounds. The normal ammunition mix is 31 APDS, 26 HESH/HEP, and three smoke rounds. The gunner also has the telescope with a magnification of x8 available. Four 76mm smoke mortars are mounted to each side of the turret and can be fired either as single rounds or in salvo. The engine compartment is at the rear, separated from the fighting compartment by a fire proof bulkhead. The engine is normally run on diesel fuel (NATO designation F-54), consuming about 190 liters per 100km. A total capacity of 1010 liters, reduced to 985 liters on later Leopards. The Leopard 1 is able to ford water obstacles 1.20m deep (wading) without any special preparations or loss of combat effectiveness. For fording at a depth of 2.25m (deep-wading) about ten minutes of special preparation is needed to seal the tank.
Leopard 1A1
After 4th batch of tanks was delivered a modernization program was launched in 1970 to enhance the combat effectiveness of the Bundeswehr’s existing fleet. Most importantly, all Leopards received the Cadillac-Gage main gun stabilization system. Targets could now be acquired and engaged on the move, and the system significantly increased the probability of a first-round hit in a tank duel. The Leopard 1A1 also added the now-famous “skirts” along the sides to protect the upper tracks. Between 1974 and 1977 all of the machines in the first four batches were brought to the same Leopard 1A1A1 standard and given additional turret armor developed by Blohm & Voss.
Leopard 1A2
The Leopard 1A2 Tank is quite difficult to distinguish from the modernized Leopard 1A vehicles of the 4th batch. The Leopard 1A2 never received add on turret armor, but it did get an improved NBC protection system. The first 232 tanks of the fifth production batch were delivered with a cast steel turret of thicker armor and were designated as the Leopard 1A2 between 1972 and 1974.
Leopard 1A3
LEOPARD 1A3 The remaining 110 vehicles from the fifth batch were fitted with a new welded turret incorporating spaced armor and a wedge-shaped gun mantlet. Although the degree of armor protection remained unchanged, the internal volume of the turret was increased by 1.5 m2. The improved TRP 2A independent sight was installed for the commander. Upgrades were identical to the 1A2 models.
Leopard 1A4
The Bundeswehr took delivery of the first 250 vehicles from the sixth batch in 1974, designated Leopard 1A4. This version had the welded turret introduced with the Leopard 1A3, but with a new integrated fire control system.
Leopard 1A1A1
From 1975 to 1977 all vehicles in the 1st to 4th batches, known as the Leopard 1A1 were retrofitted with additional turret armor developed by Blohm und Voss. The armor consists of steel plates with a two-faced rubber lining, being attached to the turret with shock-proof spacers and nuts. The gun mantlet received a wedge-shaped, add-on armor made of steel plates. Following modification, the vehicle was re-designated Leopard 1A1 A1. The add-on armor increased combat weight to 42.4 tonnes.
Leopard 1A5
In 1980 a research program was undertaken to study further improvements to Leopard 1, the aim being to maintain its survivability and combat effectiveness beyond the year 2000. it was planned to convert some 1,225 Leopard 1A1 A1. Tanks form 1st to 4th batches. In the event, one vehicle was destroyed by fire, reducing the eventual total to 1,224. Re-designated Leopard 1A5, the first modified vehicle was delivered to the Bundeswehr in early 1987. Since then, almost all users of the Leopard 1 have also applied similar changes to their own vehicles, and in most ways, the 1A5 be considered the “standard” Leopard 1 today.
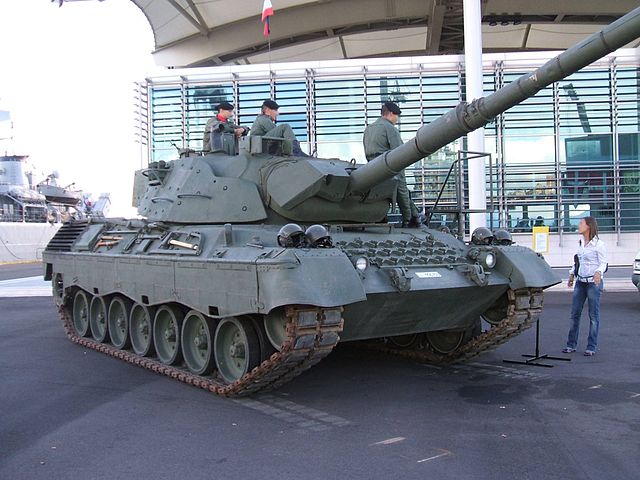

Leopard 1A6
The Leopard 1A6 prototype was a single Leopard 1A1A1 testbed. This model was modified with additional armor on the turret, and equipped with a 120 mm L/44 gun. At that time Leopard 2 was in widespread service and the modification 1A5 offered a more reasonable upgrade path for a fraction of the cost. The project was ended in 1987.
Modified and derivative vehicles
Leopard 1 Driver Training Tank
In addition to theoretical education and simulator training, the Bundeswehr utilizes 60 Leopard 1 driver tanks delivered between 1978-79 by Krauss-Maffei. The turret is replaced by an observation cabin with a dummy gun. The instructor, with appropriate devices to override the trainee driver like in-car school driving.
Bergepanzer 2 Standard Armoured Recovery Vehicle
When the development of Leopard 1 began the need for a capable ARV was immediately recognized, as was the need for maximum commonality with the new MBT. The detailed design of the ARV started in 1962, headed by Porsche, and the first two prototypes were ready in 1964. After successful trials in 1965 production of the Bergepanzer 2 started. The first vehicle of 444 built being delivered in September 1966. Bergepanzer 2 replaced the obsolete M74 and a number of M88s.

Pionierpanzer 1 Armoured Combat Engineer Vehicle
The vehicle being duly designed by Porsche in 1966 to fill the need for a special ACEV. Production of 36 vehicles for the Bundeswehr commencing one year later. Officially designated Bergepanzer 2A1, the vehicle is based on the ARV and special equipment includes an auger, stored on the engine deck, fitted to the crane jib, and hydraulically operated. The Pionierpanzer 1 is also equipped with electric cutting and welding equipment. The crane jib incorporates a ladder. All 36 Pionierpanzer 1 in German service were converted into Pionierpanzer 2 Dachs (Badger).
Bergepanzer 2A2 Armoured Recovery Vehicle
Following the demands of units equipped with the Leopard 2 and Gepard for an increased lifting capability, in 1978 MaK System delivered 100 improved ARVs. Improvements included an enhanced NBC protection system.
Pionierpanzer 2 Dachs Armoured Combat Engineer Vehicle
The German army was trying to find a low-cost solution and from 1981 to 1985 the Pionierpanzer 2 Dachs was developed. MaK System of Kiel was awarded the production/conversion contract. In April 1989 the first series vehicle of 140 ordered was handed over to Bundeswehr.
Bruckenlegepanzer 1 Biber Bridgelayer
The development program for a bridgelayer based on a modified Leopard 1 chassis started in 1965, and in 1969 two prototypes were ready. The first of 105 Bruckenlegepanzer 1 Biber (Beaver) AULB were delivered in 1975. The Biber has a crew of two, the driver and the commander.
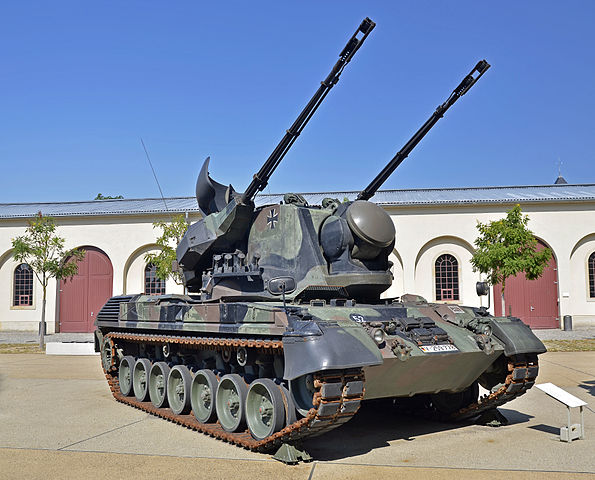
Flakpanzer 1 Gepard
In 1965 a development program was started for a new self-propelled air defense gun system for the Bundeswehr. In 1973 an order for 420 Gepards was placed for the Bundeswehr. The First 195 vehicles, known as the (5PZF-) B2 and designated Flakpanzer 1 Gepard, were delivered, the remaining 225 were fitted with a Siemens laser range finder on top of the tracking radar radome installed to the turret front and are known as the (5PZF-) B2L, designated Flakpanzer 1 Gepard A1.

Current Leopard 1 main battle tank operators

Brazil

Chile

Ecuador

Greece

Lebanon

Turkey
Current Leopard 1 specialist variant operators

Denmark

Finland

Italy

Netherlands

United Kingdom
Former Leopard 1 operators

Australia

Belgium

Canada

Germany

Norway